Symbol: C
Atomic number: 6
Atomic mass: 12
Electronic configuration: 1s2, 2s2 2p2
Valency: 4
Occurrence: it occurs both in free state(graphite, diamond) and combined state (CO2, organic compound, bicarbonates, carbonates)
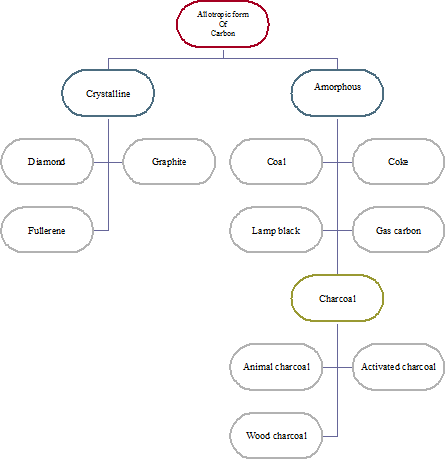
Allotropic forms of carbon
Some elements are found in nature in different physical states (form) having similar chemical properties but different physical properties. Such different forms of an element are known as its allotropes and the phenomenon is known as allotropy. Allotropes of carbon are classified into two classes:
- Crystalline form
- Amorphous form
They are further classified and shown below:
Classification of allotropes of carbon
Diamond
In diamond all the c-atoms are sp3 hybridized and arranged tetrahedrally by forming three-dimensional networks of covalent bonds having each angle 109028‘ and each C-C bond length 1.54A0. These covalent bonds are very strong and compact which makes diamond as the hardest substance with high melting and boiling point. During bond formation all the four valence electrons are used and no electrons are left, due to absence of free electrons diamond is bad conductor of heat and electricity.
Properties:
- It is one of the hardest substance known.
- It is the purest and most dense form of carbon. Its density is 3.51 at 150C.
- It has high refractive index value (2.45), hence it is valued as a gem.
- The pure form is colorless and is transparent to X-rays.
- The exceptional hardness and density of diamond can be explained on account of its structure.
- It is almost inactive towards chemical reaction but gets oxidized to CO2 when it is heated up to 9000C in presence of air.
- It changes to graphite above 18000C.
Uses:
It is used as a jeweler; black diamond is used for cutting glass and in polishing other diamonds.
Graphite
Graphite has two dimensions layer structure. In these layers each carbon atom is sp2 hybridized C-atom by forming planner hexagonal rings with each bond angle 1200and each C-C bond length is 1.42A0. The two adjacent layers is separated by distance 3.4A0 and linked by vander walls force of attraction. Hence, in graphite one layer can slide down over other which makes it soft, slippery in nature. In graphite only three valence electrons are used to form covalent bond, due to the presence of one free electron in each C-atom graphite acts as good conductor of heat and electricity.
Properties:
- It is a grey-black, soft crystalline with metallic luster.
- It is so soft that it’s soapy to touch and marks the paper, hence it is also called ‘black lead’.
- It is lighter than diamond (sp. gr. =2.2) and is good conductor of heat and electricity.
- It resists the effect of heat and isn’t acted upon by dilute acids or alkalis.
- With conc. HNO3, it gives graphite acid (C11H4O5), a greenish yellow insoluble acid.
- The softness and conductivity of graphite can be explained on account of its structure.
Uses:
It is used in manufacture of lead pencils, in making electrodes, as a lubricant in the form of aqua-dag or oil-dag, to make crucibles and as a resistance in electric furnaces.
Fullerenes:
Fullerene is the third crystalline new allotropic form of carbon discovered by Kroto and Smalley in 1985. It was named as Buck minister fullerenes. The most common fullerene is C60 (which contains 60 C-atom). The shape of C60 fullerene is spherical same as soccer ball so, it is also called Bucky ball. It has polygon system which contains fused five or six member rings of C-atom. Each C-atom is sp2 hybridized. It is covalent in nature and soluble in organic solvent.
Uses:
It is used as super conductor; to manufacture new type of polymer; as sieve (tube like structure).
Coal:
Coal is hard black solid which is obtained naturally by carbonization process. Carbonization is the slow process of conversion of plant matters (wood) into coal under the influence of high temperature and pressure in the absence of air.
Uses:
- It is used as fuels.
- Coal is used to manufacture graphite, coke, gas carbon, coal gas, etc.
- It is used to manufacture synthetic petrol by catalytic hydrogenation.
Charcoal:
Charcoal is black, soft and highly porous amorphous, allotropic form of carbon. It is obtained by destructive distillation of animal and plant materials. Charcoal is classified into various types depending upon their source of origin.
Bone charcoal èbone
Wood charcoal èwood
Sugar charcoal èsugar
Uses:
- It is used as fuel.
- It is used for purification of drinking water.
- It is also used for refining sugar.
- It is used for making gun powder.
Activated charcoal
The absorption capacity of charcoal is increased by passing high-temperature steam over it in vacuum. During the process, the surface area of pores of charcoal is increased and all the initially absorbed gases are removed and the obtained charcoal is called activated charcoal. It is mainly used to manufacture gas mask.
Lamp black
It is black, soft, velvety powder which is obtained by heating coal tar or oily organic compound in limited supply of air.
Uses:
- It is used as a black paint.
- It is used for manufacturing shoe polish.
- It is also used for making printer inks.
Coke
Coke is a residue obtained by destructive distillation of pure coal. It is used as a fuel, it burns without smoke. It is used as reducing agent in metallurgy.
Gas carbon
It is black solid deposited on the walls or roof of retort (chimney) during destructive distillation of coal. It is also pure form of carbon and good conductor of electricity.
Uses:
- It is used in battery.
- It is used for manufacture of crucibles.
- It is also used for making leads of pencil.


Top comments (0)