Isomerism
Compounds having same molecular formula but different structural formula and differ from each other in physical and chemical properties are known as “Isomers” and this phenomenon is called “isomerism”. Isomerism is due to the difference in the arrangement of atoms in molecules.
Types of isomerism
Isomerism can broadly be divided into two main classes:
- Structural isomerism
- Stereo isomerism
1. Structural isomerism
When isomerism is due to the difference in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, without any reference to space, the phenomenon is referred to as “structural isomerism”.
Structural Isomerism is of five types:
- Chain Isomers
- Position Isomers
- Functional Isomers
- Metamerism
- Tautomerism
Chain isomerism
Chain isomers have same molecular formula but differ in the order in which C-atoms are bonded to
each other.
Example:
(n-butane)n_butane Iso-butane
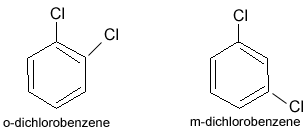
Position isomerism
Isomerism caused by the difference in the position of functional group in the same chain is termed as position isomerism.
Example:
Functional isomerism
Functional isomers have same molecular formula but different functional group.
Example:
Metamerism
This type of isomerism is due to the unequal distribution of carbon atoms on either side of functional group. Metamerism belongs to same homologous series.
Example:
Tautomerism
It is a special type of functional isomerism in which the isomers are in dynamic equilibrium with each other.

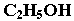
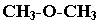
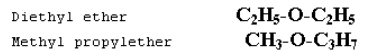

Top comments (0)