Eqv. Mass of A / Eqv. Mass of B = Mass of A / Mass of B
This relation tells that the combining mass reactants is always in the ratio of their equivalent mass. This law is also known as LAW OF CHEMICAL EQUIVALENCE.
Atomic Mass = Eqv. Mass X Valency
‘Gram Eqv.’ or ‘Eqv.’
Eqv. mass of a substance, expressed in gram is ‘one gram equivalent’ or ‘1 eqv.’
- Equivalent Mass of a compound
a) Eqv. mass of acid = Molecular Mass of acid / Basicity
where Basicity of an acid is defined as no. of H+ ions displaced or OH- ions combined per molecule of the acid.
Eqv. mass of H2SO4 = 98 / 2 = 49
b) Eqv. mass of Base = Molecular Mass / Acidity
where acidity of the base is defined as the no. of H+ ions consumed or OH- ions displaced per molecule of the base.
Eg.
Eq. Mass of Ca(OH)2 = 74/2 = 37
c) Eqv. mass of Salt = Molecular Mass of Salt / Total no. of charge in basic or acid radical per molecule
Eg.
Eq. mass of Na2CO3 = 106 / 2 = 53

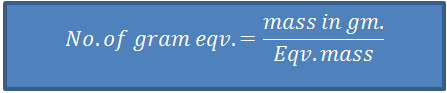

Top comments (0)