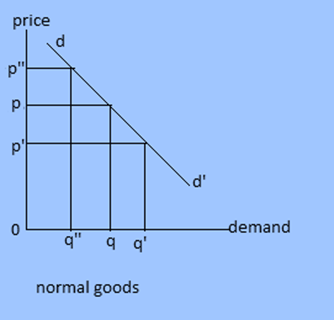
1. Price demand : Demand primarily dependent upon price is called price demand. This demand is sensitive or responsive to the change in price. In case of normal goods, demand increases with fall in price and vice versa. But in case of giffen goods demand increases even there is rise in price.
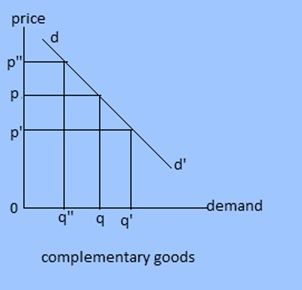
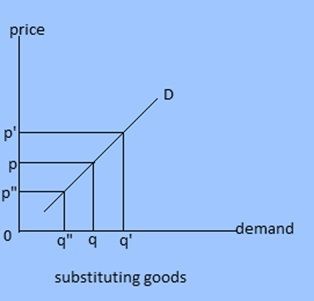
2. Cross demand : Demand primarily dependent upon prices of related goods is called cross demand. The complementary goods and substitutes are called related goods. In case of complementary goods like pen and ink demand for good is inversely related to the prices of other goods but the case in substituting goods are just opposite. Demand for substituting goods is directly related to prices.
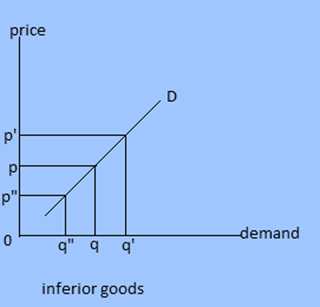
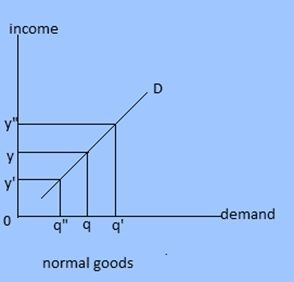
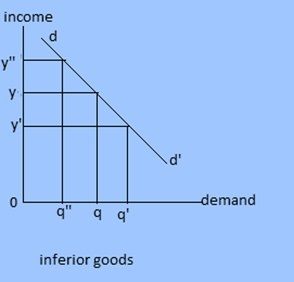
3. Income demand: Demand primarily dependent upon income is called income demand. This demand is sensitive or responsive to the change in income. In case of normal goods, demand increases with rise in income and vice versa. But in case of giffen goods demand decreases when there is increase income.
4. Direct demand : Demand for goods and services made by final consumers to satisfy their wants or needs is called direct demand. For example guest of hotels make the demand for food.
5. Derived demand : Demand for goods and services made according to direct demand is called derived demand. For example demand made by hotels for vegetable, groceries is called derived demand.
6. Joint demand : Demand made for two or more goods and services to satisfy single need or want is called joint demand. For example, tea sugar are demand together to satisfy a single need. The complementary goods are jointly demanded.
7. Composite demand : Demand for a single commodity made in order to use for different purposes is called composite demand. In this case, commodity is one but the number of uses is multiple. For example, the electricity is used for lighting, heating, transportation for the use of different electrical device.


Top comments (0)