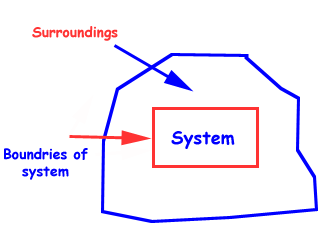
A thermodynamic system is a collection of matter which has distinct boundaries.
Or,
A real or imaginary portion of universe which has distinct boundaries is called system.
Or,
A thermodynamic system is that part of universe which is under thermodynamic study.
For example:
A balloon filled with water
A beaker filled with water
Types of system
There are three types of thermodynamic systems.
- Open system
- Closed system
- Isolated system
1. Open system
An open system is one in which both mass & energy transfer takes place across the boundaries.
- An open tank of water.
2. Closed system
A closed system in which there is no transfer of mass takes place across the boundaries of system but energy transfer is possible.
- A gas in a balloon.
3. Isolated system
An isolated system is that in which there is no transfer of mass & energy takes place across the boundaries of system.
- A thermo flask containing hot or cold liquid.
Macroscopic properties
All the properties of a system in bulk which are easily measurable are known as macroscopic properties.
Types of macroscopic properties
Macroscopic properties can be divided into two main classes.
- Intensive properties
- Extensive properties
1. Intensive properties
Macroscopic properties of a system which are independent of mass are known as intensive properties, whatever is the mass but properties remain unchanged.
For example: melting point, boiling point, density, temperature, pressure, viscosity.
Extensive properties
Macroscopic properties of a system which are strictly dependent on their mass or quantity of matter are known as extensive properties.
- If mass is halved the property will also be half. For example: volume, mole, mass, enthalpy, internal energy, kinetic energy.


Top comments (0)