To Find the volume of the given cylinder using vernier calipers.
Formula:
- Volume of the cylinder V = pi r^2 lcm^3, V= volume of cylinder, r = radius of cylinder l = length of cylinder.
- Least count of vernier calipers L.C = frac{S}{N} cm, S = value of 1 Main scale division , N = Number of vernier divisions.
- Length (or) diameter of Cylinder = Main scale reading (a) cm + ( n*L.C ) cm. n = vernier coincidence.
Procedure : First we have to determine the least count count of the given vernier calipers.
To determine the volume of the cylinder we have to determine:
- The length of the cylinder
- radius of the cylinder and substituting these values in the equation for the volume of the cylinder we can calculate it.
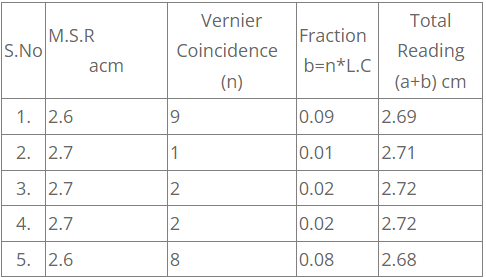
1. To determine the length of the cylinder:
Given cylinder is held gently between jaws 1,1 of the vernier calipers. The reading on the main scale just before the zero of the vernier is noted. This is called Main scale reading (M.S.R).The number of division (n) on the vernier which coincides perfectly with any one of the main scale divisions is noted.T his is called vernier coincidence (V.C).The vernier coincidence (V.C=n) is multiplied by least count to get the fraction of a main scale division. This is added to the main scale reading (M.S.R) to total reading or total length of the cylinder.
Total reading = M.S.R + (V.Ctimes L.C)
Take the readings, keeping the cylinders between jaws 1,1 at different positions. Post the values of M.S.R and vernier coincidence (n) in the table. Take at least 5 readings, get the average of these 5 readings which is mean length(l )of the cylinder.
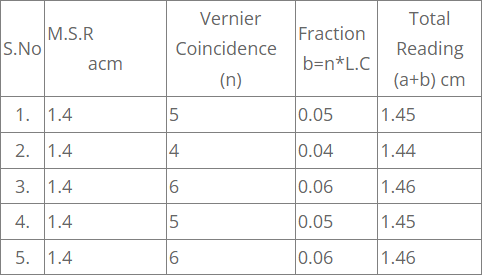
2. To determine the diameter of the cylinder: Place the cylinder diametrically between the jaws 1,1 of the vernier calipers, as in the above case post the values of M.S.R and vernier coincidence (n) in the table. Take at least 5 readings, calculate the average of these readings which gives the mean diameter ( d=2r ) of the cylinder.
3. To determine the volume of the cylinder: Substituting the values of mean length (l ) of the cylinder and mean diameter ( r) of the cylinder which is already determined, in the formula V = pi r^2 l cm^3.
Determine Least count of vernier calipers : From the given vernier calipers
S= Length of Main scale division = 1 mm = 0.1 cm,
N = Number of vernier scale divisions = 10 ,
Substitute these values in the formula of Least count L.C = frac{S}{N} = frac{0.1}{10} =0.01 cm.
Table – Length of the cylinder:
Average length of the cylinder l = frac{2.69+2.71+2.72+2.72+2.68}{5} cm=frac{13.52}{5} = 2.70 cm
Average diameter of the cylinder d = 2r = frac{1.45+1.44+1.46+1.45+1.46}{5} cm=frac{7.26}{5} = 1.45 cm,
Average radius of the cylinder r =frac{d}{2} =frac{1.45}{2} cm = 0.73 cm.
Observations:
Average length of the cylinder l = 2.70 cm,
Average radius of the cylinder r = 0.73 cm.
Calculations : Volume of the cylinder V = pi r^2 lcm^3 = frac{22}{7}times(0.73)^2times2.70cm^3 = 4.52 cm^3
Precautions:
- Take the M.S.R and vernier coincide every time without parallax error.
- Record all the reading in same system preferably in C.G.S system.
- Do not apply excess pressure on the body held between the jaws.
- Check for the zero error. When the two jaws of the vernier are in contact, if the zero division of the main scale coincides with the zero of the vernier scale no zero error will be there. If not zero error will be there, apply correction.
Result and Units: Volume of the cylinder V = 4.52 cm^3.


Latest comments (0)