Chemistry of methane
Intriduction
Molecular formula = CH4
Molecular mass = 16
Empirical formula = CH4
Empirical formula mass = 16
State: Gas at room temperature.
Occurrence: marsh, stagnant ponds.
It is the major constituent of natural gas. Natural gas contains 94.6% methane.
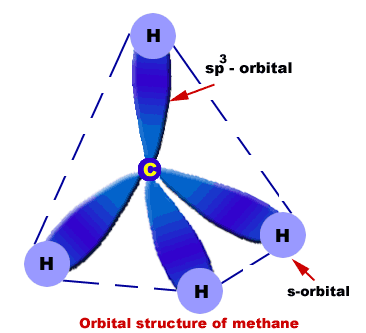
Orbital structure of methane
Composition of methane molecule:
Methane molecule consists of one carbon and four hydrogen atoms (CH4).
Nature of hybridization:
In methane C-atom is Sp3-hybridized. One s-orbital and three p-orbitals (2px,2py,2pz) of carbon atom undergo Sp3-hybridization to produce four Sp3-hybrid orbitals. These Sp3-hybrid orbitals are 109.5o apart.
Sigma bond formation:
Each Sp3-hybrid orbital overlaps 1s-orbital of H-atoms. In this way four s-bonds are produced between C and four H-atoms.
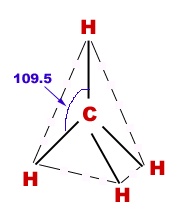
Geometry of methane:
Methane molecule is tetrahedral in structure in which carbon is central atom and four H-atoms are surrounding it in three-dimensions.
Bond angles:
HCH-bond angles are 109.5o.
Bond length:
All C-H bonds are 1.09Ao.
Method of preparation of methane
From Grignard's reagent:
Methane can be prepared by the hydrolysis of “Methyl Magnesium Iodide”.
CH3-Mg-I + HOH == CH4 + Mg-I-OH
By the catalytic reduction of methyl iodide:
CH3-I + H2 == CH4 +HI
By the reduction of methyl iodide with nascent hydrogen:
CH3I + 2[H] == CH4 + HI
By sodium acetate and NaOH:
CH3COONa + NaOH == Na2CO3 +CH4
Chemical properties of methane
Combustion reaction:
Combustion of methane is an exothermic reaction in which a large amount of energy is liberated. Due to this property, methane is used as a domestic and industrial fuel.
CH4 + 2O2 == CO2 + 2H2O
Halogenation:
Replacement of halogen atom with H-atom of an organic compound is called halogenation. It is a substitution reaction.
Chlorination:
CH4 + Cl2 == CH3Cl + HCl (chloro methane)
CH3Cl + Cl2 == CH2Cl2 +HCl (dichloro methane)
CH2Cl2 + Cl2 == CHCl3 + HCl (chloroform)
CHCl3 + Cl2 == CCl4 +HCl (carbon tetra chloride)
Mechanism
It is a photochemical reaction.
Initiation step:
In the presence of sunlight Cl2 molecule undergoes homolytic fission to produce Cl-free radical.
Cl-Cl == Clo + Clo (free radical)
Propagation step:
Chlorine free radical attacks methane molecule to produce methyl free radical.
CH4 + Clo == CH3o + HCl
CH3o + Cl2 == CH3Cl + HCl
Termination step:
This reaction comes to halt when any two free radicals combine.
Clo + Clo == Cl2
CH3o + Clo == CH3-Cl
CH3o + CH3o == CH3-CH3
Output:
Since it is a chain reaction, therefore, it gives a mixture of different compounds.
Physical properties of methane:
Methane is a colorless, odorless and non-poisonous gas.
Melting point = -182.5oC.
Boiling point = -169.5oC.
Its molecule is symmetrical.
It is lighter than air.
Uses of methane
- Domestic and industrial fuel
- Shoe polish
- Printing ink
- Tyre manufacturing
- Manufacture of methyl alcohol


Top comments (0)