Objects undergo changes in dimension when they are heated. This change in length or area or volume is called “Thermal Expansion”.
Why bodies expand on heating
At a given temperature, inter-molecular distances are definite. When a body is heated its molecules vibrate more energetically against the action of inter-molecular forces and the displacement of molecules is increased. Since the average distance between the molecules increases, the dimension of the body increases. Consequently, body expands.
Types of thermal expansion
There are three types of thermal expansion:
- Linear Expansion
- Superficial Expansion
- Volumetric Expansion
Linear expansion
Expansion in length of solid bodies on heating is called linear expansion.
Factors on which linear expansion depends
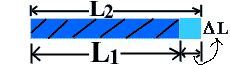
Consider a metallic bar of length “L1” at temperature “T1” k . Let the bar is heated to “T2” k.
From experiments, it is observed that linear expansion depends on two factors:
1. The increase in length of a solid bar is directly proportional to its original length
2. The increase in length is directly proportional to the change in temperature.
Where
= Coefficient of linear expansion of solid.
Final length of bar
Coefficient of linear expansion
It is a characteristic property of a material of solid and is defined as "Increase in length per unit original length per Kelvin rise in temperature is known as coefficient of linear expansion".
It is denoted by:
Its value is constant for a given material but different for different materials. It is independent of mass & dimensions of body. Coefficient of linear expansion depends on the nature of material.
Its unit is:

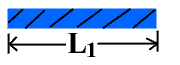
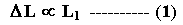
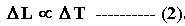
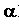
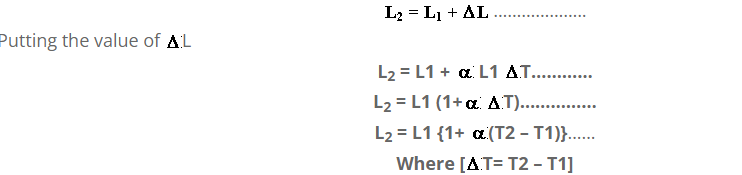
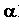
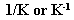

Top comments (0)