Unit Vector
“A unit vector is defined as a vector in any specified direction whose magnitude is unity i.e. 1. A unit vector only specifies the direction of a given vector."
A unit vector is denoted by any small letter with a symbol of arrow hat ().
A unit vector can be determined by dividing the vector by its magnitude.
For example unit vector of a vector A is given by:
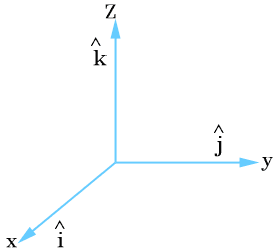
In three-dimensional coordinate system unit vectors
having the direction of the positive X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axis are used as unit vectors. These unit vectors are mutually perpendicular to each other.
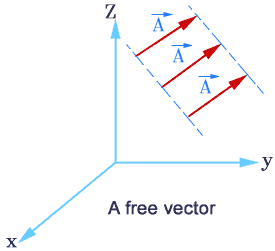
Free vector
A vector that can be displaced parallel to itself and applied at any point is known as a free vector.
A free vector can be specified by giving its magnitude and any two of the angles between the vector and coordinate axes.
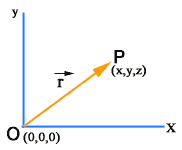
Position vector
A vector that indicates the position of a point in a coordinate system is referred to as position vector.
Suppose we have a fixed reference point O, then we can specify the position of a given point P with respect to point O by means of a vector having magnitude and direction represented by a directed line segment OP. This vector is called position vector.
In a three-dimensional coordinate system if O is at origin then, O(0,0,0) and P is any point say P(x, y,z)
in this situation position vector of point P will be:
A null vector is a vector having magnitude equal to zero. It is represented by. A null vector has no direction or it may have any direction. Generally a null vector is either equal to resultant of two equal vectors acting in opposite directions or multiple vectors in different directions.

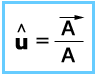
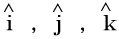
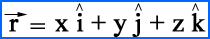


Top comments (0)