This family contains more than 600 genera and 13,000 species. It is the second largest family of dicotyledons. The members of this family are cosmopolitan in distribution. This family is divided into 3 sub-families:
- Papilionaceae
- Mimosaceae
- Caesalpiniaceae
Papilionaceae
This family is the largest of 3 families of legumihosae. It includes 375 genera and 7000 species.
Distribution:
The members of this family are distributed in the temperate region of both northern and southern hemisphere.
Habit and Habitat:
Herbs, shrubs, often climbing or twinging trees, most of the members are cultivated for pulse and green manuring.
Root:
Tap root, branched, bear nodules containing fixing bacteria.
Stem:
Herbaceous or woody, erect, twinging or climbing (e.g. Pisum), branched, cylindrical or angular or flattened, hairy in few forms.
Leaf:
Canline and ramal, alternate rarely stipulated opposite or whorled, petiolate, compound (generally pinnetely compound) or sometimes, simple (e.g. Crotolaria), modified into tendrilion some plants (e.g. pisum), sleep movement are common.
Inflorescene:
Racemose-raceme or spike or head (e.g. Trifolium)
Flower:
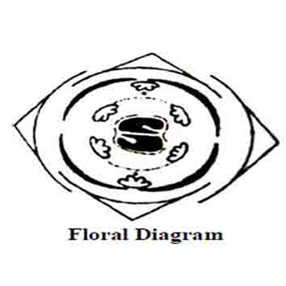
Pedicellate, brecteate or ebracteate, zygomorphis hermaphrodite(bisexual), complete, pentamous, hypogynous or perigynous, papilionaceous.
Calyx:
Sepals-5, gamosepalous, equal or unequal, campanulate or toothed, ascending imbricate aestivation(odd sepal anterior), may be persistent, inferior.
Corolla:
Petals-5, polypetalous, unequal, the uppermost posterior and the largest petal is known as standard or vexillum; two free lateral petals are known as wings or alae; this anterior pair of united petals is termed as keel or carina, this encloses stamens and pistil; venation is conspicuous, aestivation descending imbricate (vexillary), inferior.
Androecium:
Stamens-10, rarely free, diadelphous, nine in one bundle and one posterior free, anther-dilhecous, basifixedor dorsifixed, introse.
Gynoecium:
Monocarpellary, ovary superior, stalked or sessile, unilocular, ovules margin marginal placentation, style bent, hairy, stigma simple.
Fruit:
Legume or pod, sometimes lomentum.
Pollination:
Entomophilous, self or cross-pollination
Seeds:
Many, exalbuminous
Diagnostic feature of family papilionacea:
- Root: Roots are tap-root type, root possesses nodules containing nitrogen fixing bacteria(Rhizobium)
- Leaf: stipulated, stipule often folliaceous
- Flower: Zygomorphic, pentemerous
- Calyx: Sepal-5, gamosepalous, unequal, persistent, ascending imbricate aestivation
- Corolla: Petals-5, polypetalous, papilionaceous, descending imbricate or vexillary aestivation
- Stamen: Stamens-10, diadekohous (arranged in 2 bundles) 9+1
- Ovary: monocarpiallary ovary, unilocular, many ovules in locule, marginal plauntation
- Fruit: legume or pod
Economically important species of papilionaces:
- Pisum sativum : pea use : pulses
- Cicer arietinum : chana use: veg
- Phaseolus vulgaris : Simi use: veg
- Phaseolus mungo : mas
- Dalbergia sissoo : sisau use: timer
- Ptericarpous marsupium : bijaya sal use: timber
- Pterocarpous santalinus : rakta chandan use: timber
- Glycine max : soyabean
Classification:
Kingdom : Plantae
Sub-kingdom : Phanerogamea
Division : Angiospermeae
Class : Dicotylrdonae
Sub-class : Polypetalae
Series : Calyciflorae
Order : Rosales
Family : Leguminousae
Sub- family : Papilionaceaeuu


Top comments (0)