The variation of rate or reaction on temperature is given by Arhenius equation. This eqn is:
where,
k = Rate constant
Eact = Activation energy
R = Universal gas constant
T = Temperature in Kelvin
A = Constant called Arhenius factor
In a graph of lnk is plotted against 1/T it gives a straight line having y-intercept value lnA and slope -Eact/RT.
This shows that the rate constant is directly proportional to rate of reaction increase in temperature causes increase in rate of reaction.
If k1 and k2 are rate constant of a given reaction at T1 & T2.
Then,
From equation (i) and (ii) we get,

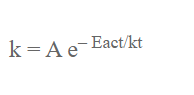
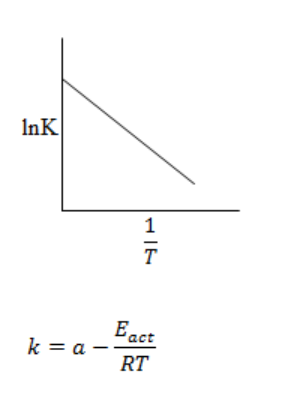
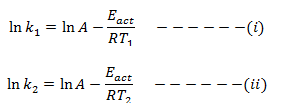
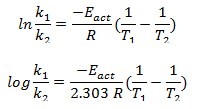

Top comments (0)