Concentration of solution corresponds to the amount of solute present in the given amount of solution. There are different units to explain the concentration of solution.
Units of concentration:
1. Percentage of solution:
It is the no. of part of solute present in 100 parts of solution. Percentage of solution can be expressed either in W/W, W/V or V/V
2. Normality of Solution (eqv.l-1 or N)
It is defined as the no. of gram eqv. of solute present in 1L of its solution.
Mathematically,
A solution is said to have concentration 1 normal (1N), decinormal (N/10) and centinormal (N/100) as 1,0.1,0.01 gm eqv. Of solute are present in 1L of solution respectively.
3. Molarity of solution (moml L-1 or M)
It is defined as the no. of g. mol. Of solute present in 1L of its solution.
Mathematically,
A solution is said to have concentration 1 molar (1M), decimolar (M/10) and centimolar (M/100) as 1, 0.1 and 0.01 g. mol. Of solute are present in 1L of its solution respectively.
4. Gram/L (gL-1)
It is defined as the no. of gm of solute present in 1L of solution. gL-1 can be related to normality (N) and molarity (M) ad thereby normality and molarity can be related to one another and it is reduced as follows:
gL-1 = Normality x eqv. wt. → 1
Similarly,
gL-1 = molarity x mol. Wt. → 2
then from equation 1 and 2. We get,
Normality x eqv. wt. = molarity x mol. Wt.
This expression says, normality and molarity of solution becomes identical only if eq. wt. and mol. wt. are same.
5. Molarity (mol Kg-1 or m)
Molarity is defined as the no. of moles of solute present in 1 kg. of solvent.
Mathematically,
A solution is said to have 1 molar concentration when 1 mole of solute is present in 1 kg of solvent.
6. Mole Fraction (x)
Mole fraction is the fraction of total no. of mole of a compound present in the mixture.
Let us consider a solution containing n1 mole of solvent and n2 mole of solute.
Here, x1 + x2 = 1
7. Part per million (PPM)
Part per million is the no. of part of solute present in 1 million part of solution.

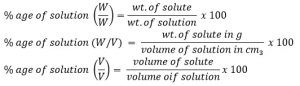
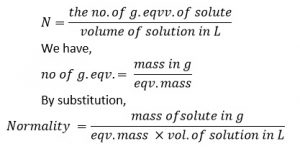
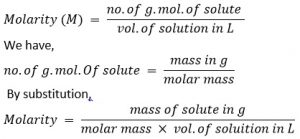
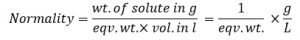
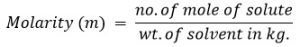
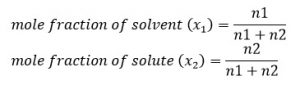


Top comments (0)