The principal ore of copper is copper pyrite and copper is extracted from this ore. The different steps in extraction of copper are:
Crushing and concentration:
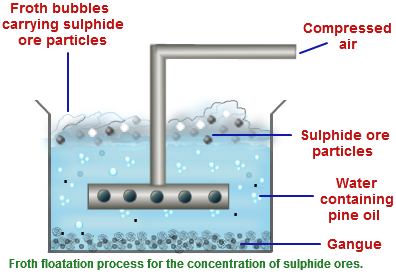
The ore obtained from mines are broken down into small piece by jaw crusher and then pulverized. The ore being sulphide ore is concentrated by froth floatation process. Pulverized ore is kept in water containing pine oil and the mixture is agitated by passing compressed air. Ore forms froth with pine oil and comes to the surface and is skimmed off while impurities are left in water.
Roasting
The concentrated ore is heated in excess supply of air on the hearth of reberberatory furnace below its melting point. The different changes during roasting are:
- Moisture and volatile impurities are driven out.
- Non-metallic impurities like sulphur, phosphorous, arsenic etc. are removed as their oxides.
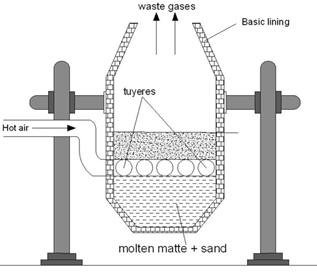
Smelting
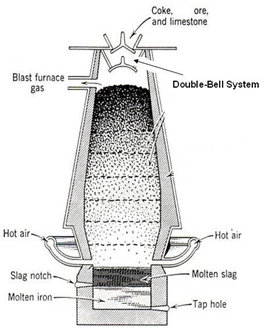
The roasted ore, coke and silica (flux) is charged a water jacketed blast furnace when hot air is passed into blast furnace. Fes if oxidized to FeO which combines with S1O2 to form ferrous silicate as slag.
As long as Fes is present in the mixture Cu2O can’t be formed as copper has higher affinity for sulphur than oxygen. In molten state FeS & Cu2S are missible and the molten mixture of Cu2S and FeS is called copper malte. The lower end of blast furnace has two openings for slag and copper matte.
Fig: Blast Furnace for extraction of copper
Bassemerisation
The molten matte is mixed with little silica and charged into a Bessemer converter. Lined internally by basic lining of CaO or MgO. Hot air is blown into the mixture which converts remaining FeS. To FeSiO3.
The reaction is highly exothermic and copper obtained is in molten state. During solidification, SO2 escapes forming blisters on the surface of metal. This variety of copper containing about 2% of impurity is blister copper.
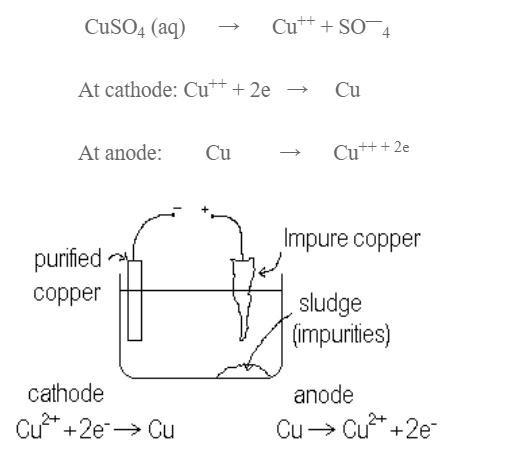
Refining:
Blister copper consists of about 2% of impurities consisting of cliver, Glod, Zinc, Nicket etc. It is mostly purified by electrolytic method. A block of impure copper is anode, a strip of pure copper is cathode while solution of CuSO4 containing dil H2SO4 is e;ectrolyte. On passing current, impure copper dissolves and equivalent amount of pure copper is deposited at cathode. Impurities are collected below anode as anode mud.
Physical Properties:
- It is a transition metal having characteristic red color.
- It is highly malleable & ductile and has high electrical and thermal conductivity
- It has high melting point 10830c and bpt 2320c
- It has specific gravity 8.93
Chemical properties
Action of air:
Dry air has no effect but moist air containing CO2gas forms a green layer of basic copper carbonate.
Action of water:
Water has no effect on copper.
Action of Alkalis:
Alkalis has no effect on copper.
Action of Acids:
** 1. With HNO3**
dil HNO3 does not react with copper while moderately conc. HNO3 (1:1) is reduced to Nitric oxide by copper.
2. With H2SO4
dil. H2SO4 alone does not react but hot dil. H2SO4 in presence of air gives CuSO4
3. With HCl
Copper reacts with hot and conc HCl in presence of air forming cupric chloride.
Displacement reaction:
Copper can displace metals lying below it in electrochemical series from their salt solution.
Uses of copper:
- It is in making electrical cables.
- It is used in making coins.
- It is used in making allays like brass, German Silver.
- It is Rold Gold, constantan, bell metal etc.
- It is used in making utensits.
- It is used in making scientifi equipments like calioriemeter boilers etc.

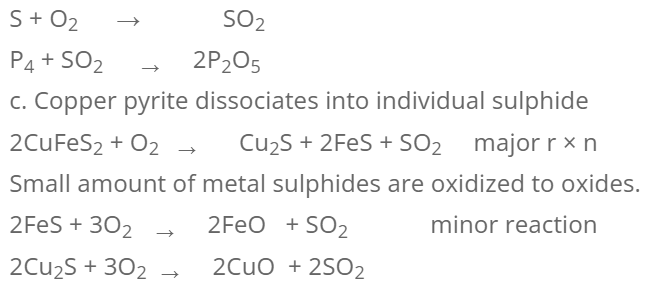

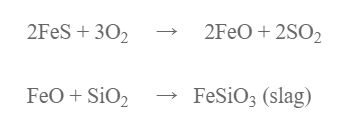







Top comments (0)