Let’s consider a reaction,
A + B → product
The rate of reaction of above reaction is given by rate law expression,
Rate:
where k is constant called rate constant and is rate of reaction when concentration of all reactants is unit molarity (1m). Here m is order of reaction with respect to A, n is order of reaction w.r.t B and (m +n) is overall order of reaction. So, order of a reaction is the sum of the power to which the concentration of reactants is raised in the experimental rate law expression.
Unit of rate constant
Let’s consider a reaction,
A → product
The unit of rate constant depends upon the order of reaction.
For a reaction,
A → product
The rate law expression is,
when n = 0 The reaction is said to be a zeroth order reaction and for such reaction the rate of reaction is independent of concentration of reactant.
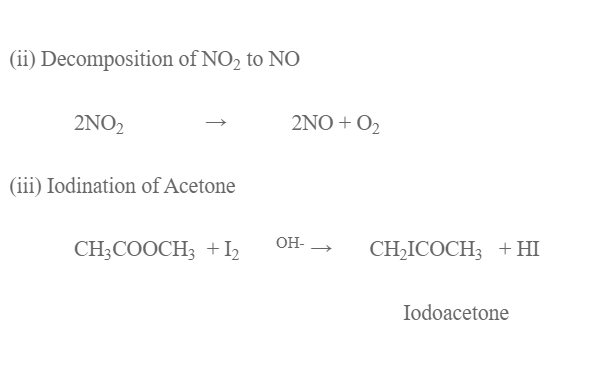
E.g.
- Enzyme catalysed bio-chemical reaction.
- Decomposition of HI on the surface of gold.
- Reaction between H2 and Cl2 to give HCl in presence of light.
When, n =1,
The reaction is said to be a first order reaction and for such reaction the change rate is equal to the change in concentration of reactant.

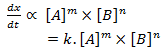
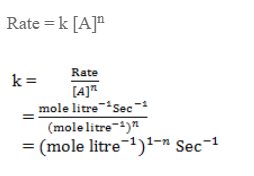

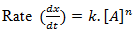



Top comments (0)