General Method of Preparation of Alkanes (Paraffins):
Alkanes can be prepared by the following methods:
- From unsaturated Hydrocarbons
- From Haloalkanes
- By Wurtz Reaction
- By reduction
- By the Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
- From Grignard’s Reagent
- From salts of Carboxylic acids
- By Kolbe’s electrolytic method
- By Heating Na-salt of Carboxylic acid
- From Metal Carbides
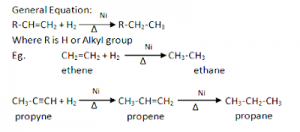
1. From unsaturated hydrocarbons
Alkanes can be prepared by the catalytic hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons in the presence of catalyst ‘Ni’ or ‘pt’ at 200⁰C to 300⁰C.
2. From Haloalkanes
By Wurtz reaction:
When alkyl halides are heated with sodium metal in the presence of dry ether, alkanes are obtained (generally having double number of C-atoms than in alkyl halides). This reaction is known as Wurtz reaction and used for the preparation of symmetrical alkanes.
By reduction of alkyl halides (RX)
Haloalkanes (R-X) when heated with reducing agents like: LiAlH4/ether, Pd/H2, Pt/H2, Zn/conc. HCl, alkanes are produced.
3. By the reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced into alkanes in the presence of reducing agents: amalgated zinc and conc. HCl.
4. From Grignard’s Reagent
Hydrolysis of Grignard’s reagent in the presence of ether gives alkanes.
dry ether
RMgX + H2O —————> R-H + Mg(OH)X
alkyl magnesium halide (alkane) (Hydroxy magnesium halide)
5. From salts of carboxylic acid
By Kolbe’s electrolytic method
Electrolysis of aqueous conc. solution of sodium or potassium salt of carboxylic acid gives alkanes.
- RCOONa—-Sodium salt
- RCOOK—–Potassium salt
RCOONa——–> RCOO– + Na+
anion cation
During electrolysis:
Electrode reaction occurs as
At anode:
RCOO– – e ——–> RCOO ———> R-R + 2CO2
unstable alkane
At cathode:
Na+ + OH– ———> NaOH
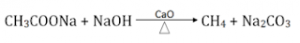
By Heating Na-salt of Carboxylic acid
When Na-salt of carboxylic acid is heated with soda lime (NaOH & CaO), alkane is obtained having one carbon less than salt by removal of a molecule of CO2. This reaction is also known as decarboxylation.
Eg:
Sodium ethanoate (methane)
This is the principle reaction for laboratory preparation of methane gas.
6. From metal carbides
Metal carbide like aluminium carbide (Al4C3) and beryllium carbide (Be2C) reacts with pure water to produce methane.
Al4C3 + 12H2O ———-> 4Al(OH)3 + 3CH4

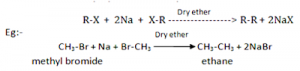


Top comments (0)