1. Calculate the heat of formation of napthalene from the following data.
Alternate solution:
Considering combustion of Napthalence, we have,
H reaction = H formation products – H formation preactants.
-1231.6 = (10 × H formation CO2 + 4 × H formation O2)
-1231.6 = {10 × (-94.405) + 4 × (-68.3)} – H formation of GoH8-O
-1231.6 = -944.05 + (-273.2) – H formation of GoH8
-1231.6 + 944.05 + 273.2 = – H formation of GoH8
-14.35 = – H formation of GoH8
H formation of GoH8 = 14.35 Kcal Jxole-1
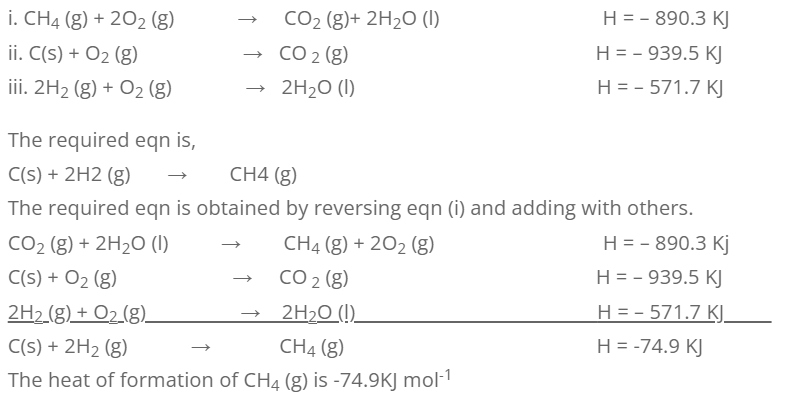
2. Calculate the standard heat of formation of CH4 (g) from the following information.
3. Calculate the enthalpy of formation of ethane at 298k, if the enthalpies of combustion at CH2 and C2 H6 are -94.14, -68.47 and -373.3 Kcal respectively.
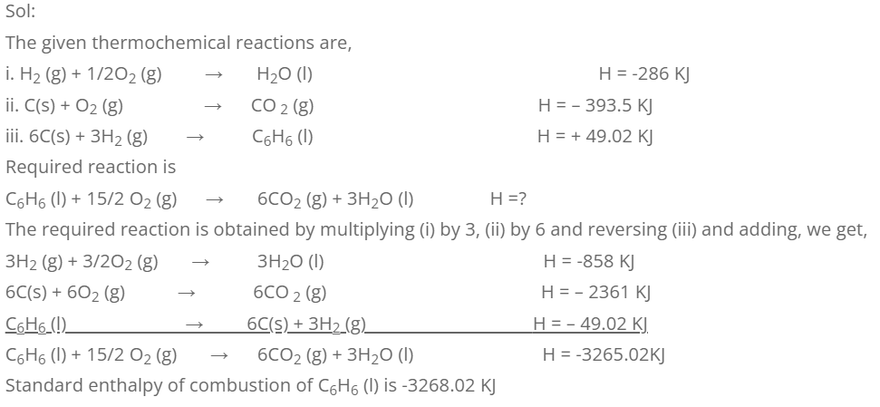
4. Standard enthalpy of formation of H2O (l), CO2 (g) and C6H6 (l) are -286, -393.5 and +49.02 KJ mol-1 respectively at 298K. Calculate the standard enthalpy of combustion of C6H6 (l) at the given temperature.
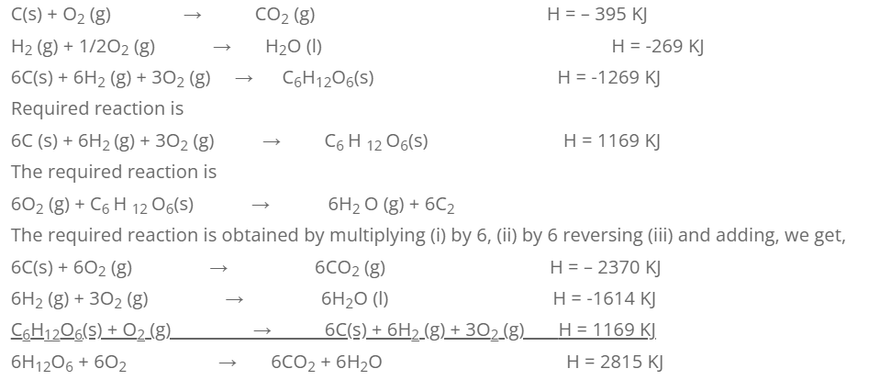
5. Calculate the heat of combustion of glucose from the following data.


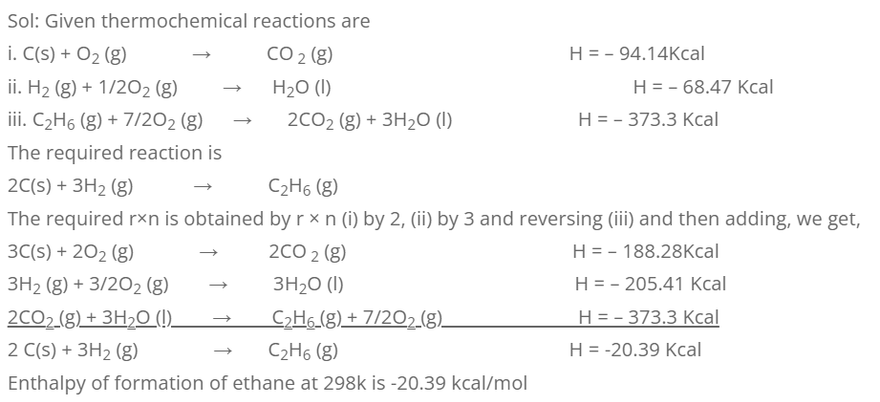

Top comments (0)