Types of computers on the basis of working principle:
- Analog Computer
- Digital Computer
- Hybrid Computer
Comparison Table
| Analog Computer | Digital Computer | Hybrid Computer |
|---|---|---|
| Analog computer operates on continuous data like temperature, pressure, speed, voltage, etc. | Digital computer operates on discontinuous or discrete data (0 and 1). | Hybrid computer is the combination of analog and digital computer. It can operate on both continuous and discontinuous data. |
| It operates by measuring and comparing. | It operates by counting and calculation. | It can convert analog data to digital and vice versa. |
| It has low accuracy. | It has higher accuracy. | In a hybrid computer, analog component is used for measuring and comparing, and digital component is used for controlling. |
| It usually contains either no any or limited storage capacity. | It usually contains larger storage capacity. | Its storage capacity varies from the application area. |
| It is special purpose computer. | It is a general purpose computer. | It is a special purpose computer. |
| It cannot be reprogrammed. | It can be reprogrammed. | |
| It can be operated only by skilled manpower. | It can be operated by general users. | It can be operated only by skilled manpower. |
| Devices like thermometer, speedometer, pressure gauge, voltmeter, etc. are the examples of analog devices. | Devices like digital watch, digital speedometer, etc. are the examples of digital devices. | |
| ‘Presley’ is an example of analog computer. | IBM desktop PC, Dell laptop, Acer notebook are the examples of digital computers. | Super computers are usually hybrid computer. |
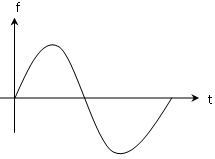
The wave form of analog computer is
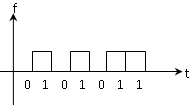
- The wave form of digital computer is
Major application areas of hybrid computers are:
- Weather forecasting
- Automated industry control
- Automated vehicles
- Rocket launching system
- Diagnosis in hospital


Top comments (0)